RESEARCH PAPER
Correlation between CD4 serum and interleukin-10 expression in placenta of HIV-positive pregnant women receiving combined antiretroviral therapy
1
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University Prof. Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah Denpasar General Hospital Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia
Submission date: 2023-08-31
Final revision date: 2023-11-27
Acceptance date: 2023-12-20
Online publication date: 2025-11-20
Corresponding author
I Wayan Artana Putra
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University Prof Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah Denpasar General Hospital Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University Prof Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah Denpasar General Hospital Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia
HIV & AIDS Review 2025;24(4):297-301
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in pregnant women affects mothers’ immune responses, with an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) is one of the specific factors that can describe the immunity of HIV-infected patients. Low levels of interleukin (IL)-10 in placental serum disrupt prostaglandin balance, causing a massive inflammatory response. The aim of this study was to assess the correlation between CD4 serum and IL-10 expression in the placenta of HIV-infected pregnant women receiving combined antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Material and methods:
This cross-sectional study used a quantitative analytic approach, and was conducted at Prof. Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah General Hospital Denpasar from May 2022 to September 2022. In this study, full-term pregnant women (≥ 37-42 weeks of gestation) with HIV infection, who have been receiving ART for at least 6 months were enrolled. IL-10 level in placenta and CD4 count in plasma were assessed. Pearson’s correlation test was applied, with a significant p-value < 0.01.
Results:
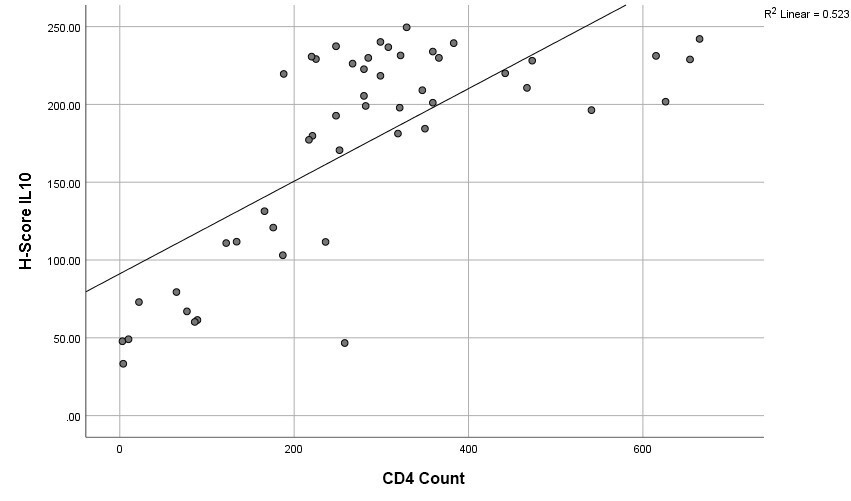
The Pearson’s correlation test results, CD4 levels, and H-score IL-10 were not influenced by the control variable. Mother's age with p = 0.000 (< 0.01) and rxy value of 0.723 was classified as a strong correlation category, with coefficient of determination rxy2 = 0.523. Analysis with controls for age, duration of treatment, and HIV stage showed significant results (p = 0.000) in correlation between CD4 count and IL-10 expression, with rxy = 0.702 and coefficient of determination rxy2 = 0.493.
Conclusions:
CD4 serum levels and IL-10 expression in the placenta of HIV-positive pregnant women on combined antiretroviral therapy, demonstrated a significant relationship.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in pregnant women affects mothers’ immune responses, with an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) is one of the specific factors that can describe the immunity of HIV-infected patients. Low levels of interleukin (IL)-10 in placental serum disrupt prostaglandin balance, causing a massive inflammatory response. The aim of this study was to assess the correlation between CD4 serum and IL-10 expression in the placenta of HIV-infected pregnant women receiving combined antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Material and methods:
This cross-sectional study used a quantitative analytic approach, and was conducted at Prof. Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah General Hospital Denpasar from May 2022 to September 2022. In this study, full-term pregnant women (≥ 37-42 weeks of gestation) with HIV infection, who have been receiving ART for at least 6 months were enrolled. IL-10 level in placenta and CD4 count in plasma were assessed. Pearson’s correlation test was applied, with a significant p-value < 0.01.
Results:
The Pearson’s correlation test results, CD4 levels, and H-score IL-10 were not influenced by the control variable. Mother's age with p = 0.000 (< 0.01) and rxy value of 0.723 was classified as a strong correlation category, with coefficient of determination rxy2 = 0.523. Analysis with controls for age, duration of treatment, and HIV stage showed significant results (p = 0.000) in correlation between CD4 count and IL-10 expression, with rxy = 0.702 and coefficient of determination rxy2 = 0.493.
Conclusions:
CD4 serum levels and IL-10 expression in the placenta of HIV-positive pregnant women on combined antiretroviral therapy, demonstrated a significant relationship.
REFERENCES (17)
1.
WHO. Global Health Observatory (GHO) data on HIV/AIDS [Internet]. WHO: World Health Organization. 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en... (Accessed: 16.06.2022).
2.
Yang M, Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Jiang Q. Impact of maternal HIV infection on pregnancy outcomes in southwestern China – a hospital registry based study. Epidemiol Infect 2019; 147: e124. DOI: 10.1017/S0950268818003345.
3.
Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th. New York, NY: Mcgraw-Hill; 2015.
4.
Mulyantari K, Retnowati E, Nasronudin N. Interleukin-10 plasma dan Limfosit-T CD4 penderita terinfeksi HIV. Indonesian Journal of Clinical Pathology and Medical Laboratory 2011; 18: 20-29.
5.
Kempton J, Hill A, Levi JA, Heath K, Pozniak A. Most new HIV infections, vertical transmissions and AIDS-related deaths occur in lower-prevalence countries. J Virus Erad 2019; 5: 92-101.
6.
Lumbantoruan C, Kelaher M, Kermode M, Budihastuti E. Pregnant women’s retention and associated health facility characteristics in the prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in Indonesia: cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2020; 10: e034418. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-034418.
7.
Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating Pregnant Women and Preventing HIV Infection in Infants: Recommendations for a Public Health Approach: 2010 Version. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
8.
Huynh K, Gulick PG. HIV Prevention. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls Publishing; 2020.
9.
Li H, Liu J, Tan D, Huang G, Zheng J, Xiao J, et al. Maternal HIV infection and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Hunan province, China: a prospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99: e19213. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019213.
10.
Faye A, Pornprasert S, Mary JY, Dolcini G, Derrien M, Barré-Sinoussi F, et al. Characterization of the main placental cytokine profiles from HIV-1-infected pregnant women treated with anti-retroviral drugs in France. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 149: 430-439.
11.
Cheng SB, Sharma S. Interleukin‐10: a pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol 2015; 73: 487-500.
12.
Kalk E, Schubert P, Bettinger JA, Cotton MF, Esser M, Slogrove A, Wright CA. Placental pathology in HIV infection at term: a comparison with HIV‐uninfected women. Trop Med Int Health 2017; 22: 604-613.
13.
Bento CA, Hygino J, Andrade RM, Saramago CS, Silva RG, Silva AA, et al. IL-10-secreting T cells from HIV-infected pregnant women downregulate HIV-1 replication: effect enhanced by antiretroviral treatment. AIDS 2009; 23: 9-18.
14.
Akoto C, Norris SA, Hemelaar J. Maternal HIV infection is associated with distinct systemic cytokine profiles throughout pregnancy in South African women. Sci Rep 2021; 11: 10079. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89551-3.
15.
Hygino J, Vieira MM, Kasahara TM, Xavier LF, Blanco B, Guillermo LV, et al. The impact of pregnancy on the HIV-1-specific T cell function in infected pregnant women. Clin Immunol 2012; 145: 177-188.
16.
Pornprasert S, Mary JY, Faye A, Leechanachai P, Limtrakul A, Rugpao S, et al. Higher placental anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokine expression in HIV-1 infected women receiving longer zidovudine prophylaxis associated with nevirapine. Curr HIV Res 2009; 7:211-217.
17.
Roberts CA, Durham LE, Fleskens V, Evans HG, Taams LS. TNF blockade maintains an IL-10+ phenotype in human effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Front Immunol 2017; 8: 157. DOI: 10.3389/ fimmu.2017.00157.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.