RESEARCH PAPER
Analysis and prediction of HIV and AIDS using machine learning: ensemble method
1
Department of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei 10608, Taiwan
Submission date: 2022-06-14
Final revision date: 2022-07-26
Acceptance date: 2022-07-28
Online publication date: 2025-07-15
Corresponding author
Minyechil Alehegn Tefera
Department of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei 10608, Taiwan
Department of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei 10608, Taiwan
HIV & AIDS Review 2025;24(4):262-266
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
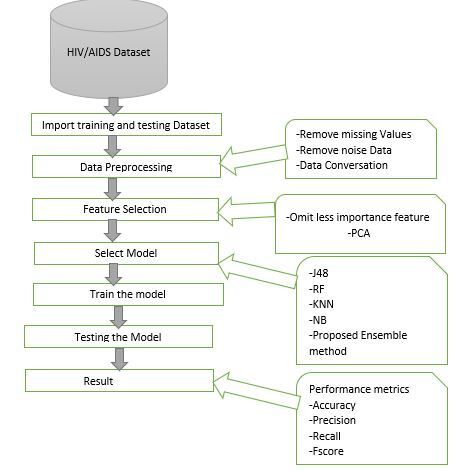
At present, especially in developing countries, human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome become very extreme. As we know, the virus break up and damages the function of immune system, and infected people gradually become immunodeficient. Artificial intelligence play a great role in the prediction of diseases. The function of immune system is the level of CD4+ cell count. In this study, ensemble method was applied.
Material and methods:
Records used in the study were collected from world data available online. Random forest, naïve Bayes, J48, and KNN algorithms as well as the proposed ensemble method using bagging technique were employed to fit the rate data, with 10k cross-validation. The performance of the model was evaluated using accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F-score.
Results:
Based on the experiment, the proposed ensemble method achieved the best results in metrics of accuracy, precision, and F-score compared with other models by providing accuracy of 95.36%, precision of 90.23%, recall of 91.5%, and F-score of 92.35%.
Conclusions:
Currently, machine learning plays a great role in the prediction of future, especially in health industry. The power of models is depending on the data. Based on the results of the study, the proposed ensemble method provided the best accuracy compared with other machine learning methods, with accuracy of 95.36% shown as very effective result.
At present, especially in developing countries, human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome become very extreme. As we know, the virus break up and damages the function of immune system, and infected people gradually become immunodeficient. Artificial intelligence play a great role in the prediction of diseases. The function of immune system is the level of CD4+ cell count. In this study, ensemble method was applied.
Material and methods:
Records used in the study were collected from world data available online. Random forest, naïve Bayes, J48, and KNN algorithms as well as the proposed ensemble method using bagging technique were employed to fit the rate data, with 10k cross-validation. The performance of the model was evaluated using accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F-score.
Results:
Based on the experiment, the proposed ensemble method achieved the best results in metrics of accuracy, precision, and F-score compared with other models by providing accuracy of 95.36%, precision of 90.23%, recall of 91.5%, and F-score of 92.35%.
Conclusions:
Currently, machine learning plays a great role in the prediction of future, especially in health industry. The power of models is depending on the data. Based on the results of the study, the proposed ensemble method provided the best accuracy compared with other machine learning methods, with accuracy of 95.36% shown as very effective result.
REFERENCES (21)
1.
Jiang F, Xu Y, Liu L, Wang K, Wang L, et al. Construction and validation of a prognostic nomogram for predicting the survival of HIV/AIDS adults who received antiretroviral therapy: a cohort between 2003 and 2019 in Nanjing. BMC Public Health 2022; 22: 30. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-12249-8.
2.
Li B, Zhang L, Liu Y, Xiao J, Li C, Fan L, et al. A novel prediction model to evaluate the probability of CD4/CD8 ratio restoration in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS 2022; 36: 795-804.
3.
Jones AJ, Eke UA, Eke AC. Prediction and prevention of preterm birth in pregnant women living with HIV on antiretroviral therapy. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2022; 20: 837-848.
4.
McKettrick P, Mallon PWG. Biomarkers to predict cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2022; 35: 15-20.
5.
Tunc H, Durdagi S, Sari M, Kotil S. ANN-based Drug-isolate-foldchange model predicting the resistance profiles of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. ChemRxiv 2022. DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-h5krl.
6.
Dong Y, Liu S, Xia D, Xu C, Yu X, Chen H, Wang R, et al. Prediction model for the risk of HIV Infection among MSM in China: validation and stability. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022; 19: 1010. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19021010.
7.
Belete DM, Huchaiah MD. Grid search in hyperparameter optimization of machine learning models for prediction of HIV/AIDS test results. Int J Comput Applications 2021; 44: 875-886.
8.
Zheng C, Wang W, Young SD. Identifying HIV-related digital social influencers using an iterative deep learning approach. AIDS 2021; 35 (Suppl 1): S85-S89. DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002841.
9.
Turbé V, Herbst C, Mngomezulu T, Meshkinfamfard S, Dlamini N, Mhlongo T, et al. Deep learning of HIV field-based rapid tests. Nat Med 2021; 27: 1165-1170.
10.
Steiner MC, Gibson KM, Crandall KA. Drug resistance prediction using deep learning techniques on HIV-1 sequence data. Viruses 2020; 12: 560. DOI: 10.3390/v12050560.
11.
Hu H, Xiao A, Zhang S, Li Y, Shi X, Jiang T, et al. DeepHINT: understanding HIV-1 integration via deep learning with attention. Bioinformatics 2019; 35: 1660-1667.
12.
Olatosi B, Vermund SH, Li X. Power of Big Data in ending HIV. AIDS 2021; 35 (Suppl 1): S1-S5. DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002888.
13.
Lu X, Wang L, Jiang Z. The Application of Deep Learning in the Prediction of HIV-1 Protease Cleavage Site. In: 2018 5th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI). IEEE, 2018; pp. 1299-1304.
14.
Luckett P, Paul RH, Navid J, Cooley SA, Wisch JK, Boerwinkle A, et al. Deep learning analysis of cerebral blood flow to identify cognitive impairment and frailty in persons living with HIV. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr (1999) 2019; 82: 496-502.
15.
Kaku Y, Kuwata T, Gorny MK, Matsushita S. Prediction of contact residues in anti-HIV neutralizing antibody by deep learning. Japanese J Infect Dis 2020; 73: 235-241.
16.
Xiang Y, Du J, Fujimoto K, Li F, Schneider J, Tao C. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning for HIV prevention interventions. Lancet HIV 2022; 9: e54-e62. DOI: 10.1016/S23523018(21)00247-2.
17.
Sun D, Peng Y, Li H. Construction of Knowledge Graph of HIV- associated Neurocognitive Disorders Syndrome based on Deep Learning. In: 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE). IEEE, 2020; pp. 134-141.
18.
Oliveira A, Faria BM, Gaio AR, Reis LP. Data mining in HIV- AIDS surveillance system. J Med Systems 2017; 41: 51. DOI: 10.1007/s10916-017-0697-4.
19.
Wang G, Wei W, Jiang J, Ning C, Chen H, Huang J, et al. Application of a long short-term memory neural network: a burgeoning method of deep learning in forecasting HIV incidence in Guangxi, China. Epidemiol Infect 2019; 147: e194. DOI: 10.1017/S095026881900075X.
20.
Shi M, Lin J, Wei W, Qin Y, Meng S, Chen X, et al. Machine learningbased in-hospital mortality prediction of HIV/AIDS patients with Talaromyces marneffei infection in Guangxi, China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2022; 16: e0010388. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010388.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.